[웹프로그래밍] Javascript #1
자바 스크립트 #1
자바스크립트(javascript): 동적인 웹 페이지를 작성하기 위하여 사용되는 언어
-
웹의 표준 프로그래밍 언어
-
모든 웹 브라우저들은 자바스크립트를 지원
자바 스크립트 특징
- 인터프리트 언어
- 동적 타이핑(dynamic typing)
- 구조적 프로그래밍 지원
- 객체 기반 – 자바스크립트는 객체 지향 언어(class도 가능)
- 함수형 프로그래밍 지원 – 즉 함수는 그 자체로 객체다(람다식도 지원).
자바 스크립트의 용도
-
HTML 콘텐츠를 동적으로 변경할 수 있다.
-
이벤트에 반응하는 동작을 구현할 수 있다.
-
HTML 요소들의 속성을 동적으로 변경할 수 있다. 즉 색상과 같은 요소들의 스타일(CSS)을 변경할 수 있다.
-
HTML 요소를 표시하거나 숨길 수 있다.
-
사용자가 입력한 값들을 검증하는 작업도 자바스크립트를 이용한다.
-
게임이나 애니메이션과 같은 상호 대화적인 콘텐츠를 구현할 수 있다.
자바 스크립트의 미래
-
자바스크립트는 본래 클라이언트 웹 페이지를 위한 프로그래밍 언어였지만 그 용도는 점점 더 확장되고 있다.
-
최근에는 Node.js처럼 자바스크립트를 서버 프로그래밍 언어로 변화시키려는 시도가 진행되고 있다.
-
결론적으로 현재의 웹 프로그래밍 기술에서 자바스크립트는 아주 중요한 역할을 하고 있다.
자바 스크립트 위치
CSS와 마찬가지로 자바스크립트도 다음과 같은 3가지 방법으로 HTML 문서에 삽입될 수 있다.
- 내부 자바스크립트
- 외부 자바스크립트
- 인라인 자바스크립트
인라인 자바스크립트만 실습을 해보자면
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
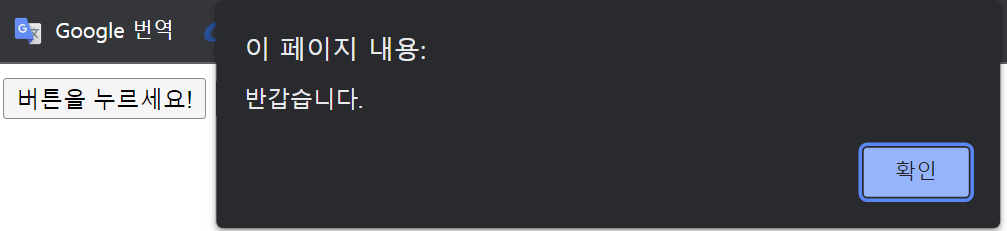
<button type="button" onclick="alert('반갑습니다.')">버튼을 누르세요!</button>
</body>
</html>
자바스크립트 코드의 위치는 다음과 같다.
- HTML 태그의 이벤트 리스너 속성에 작성
- <script></script> 태그에 작성
- 자바스크립트 파일에 작성
- URL 부분에 작성
실습
이벤트 리스너
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>이벤트 리스너 속성에 자바스크립트 코드</title>
</head>
<body>
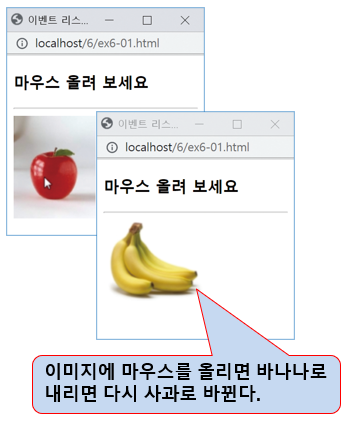
<h3>마우스 올려 보세요</h3>
<hr>
<img src="media/apple.png" alt="이미지"
onmouseover="this.src='media/banana.png'"
onmouseout="this.src='media/apple.png'">
</body>
</html>
만약 이 js를 script 태그에 작성하게 되면
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>script 태그에 자바스크립트 작성</title>
<script>
function over(obj) {
obj.src="media/banana.png";
}
function out(obj) {
obj.src="media/apple.png";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>마우스 올려 보세요</h3>
<hr>
<img src="media/apple.png" alt="이미지"
onmouseover="over(this)"
onmouseout="out(this)">
</body>
</html>
다시 자바스크립트 파일을 따로 뺴면
// filename : lib.js
function over(obj) {
obj.src="media/banana.png";
}
function out(obj) {
obj.src="media/apple.png";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>script 태그에 자바스크립트 작성</title>
<script src="lib.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>마우스 올려 보세요</h3>
<hr>
<img src="media/apple.png" alt="이미지"
onmouseover="over(this)"
onmouseout="out(this)">
</body>
</html>
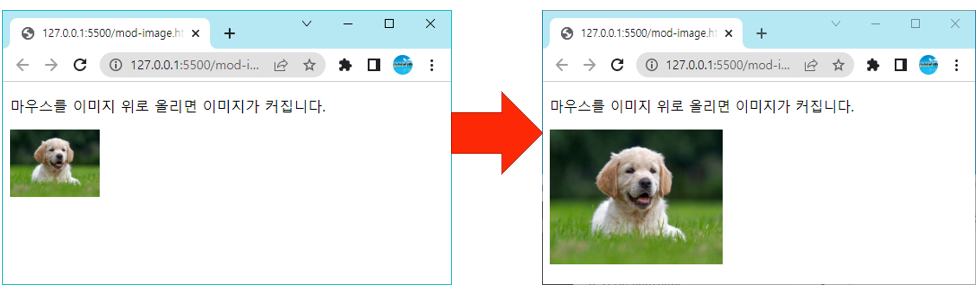
다음 실습은 마우스를 올렸을 때 그림이 커지는 코드다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>마우스를 이미지 위로 올리면 이미지가 커집니다.</p>
<img onmouseover="this.style.width='200px'" onmouseout="this.style.width='100px'"
src="dog.jpg" width="100px">
</body>
</html>
href에 js코드 작성
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>URL에 자바스크립트 작성</title>
</head>
<body>
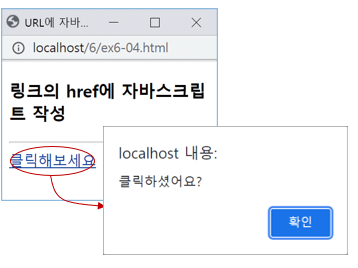
<h3>링크의 href에 자바스크립트 작성</h3>
<hr>
<a href="javascript:alert('클릭하셨어요?')">
클릭해보세요</a>
</body>
</html>
document.write 실습
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>document.write() 활용</title>
</head>
<body>
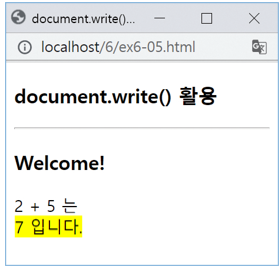
<h3>document.write() 활용</h3>
<hr>
<script>
document.write("<h3>Welcome!</h3>");
document.write("2 + 5 는 <br>");
document.write("<mark>7 입니다.</mark>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
프롬프트 다이얼로그
prompt(“메시지”, “디폴트 입력값”) 함수는 사용자로부터 문자열을 입력 받아 리턴
let ret = prompt("이름을 입력하세요", "황기태");
if(ret == null) {
// 취소 버튼이나 다이얼로그를 닫은 경우
}
else if(ret == "") {
// 문자열 입력 없이 확인 버튼 누른 경우
}
else {
// ret에는 사용자가 입력한 문자열
}
변수 사용하기
변수는 var, let const가 있다.
- var는 변수 재선언되고 업데이트 될 수 있다.
- let은 업데이트될 수 있지만, 재선언은 불가능하다.
- const는 업데이트도, 재선언도 불가능하다.
변수를 사용해 계산값을 출력해보자(출력값 : 11)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="test"></h1>
<!--id는 굳이 쓸필요 없다.-->
<script>
let x = 5;
let y = 6;
let z = x + y;
document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = z;
</script>
</body>
</html>
데이터 타입 실습
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
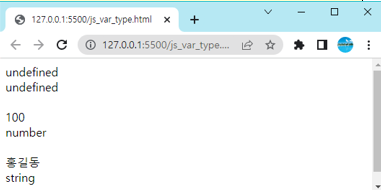
<script>
let x; // x의 값은 undefined가 된다.
document.write(x + "<br>");
document.write(typeof x + "<br><br>");
x = 100; // x은 수치값을 가진다.
document.write(x + "<br>");
document.write(typeof x + "<br><br>");
x = "홍길동"; // x는 문자열을 가진다.
document.write(x + "<br>");
document.write(typeof x + "<br><br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
지역 변수와 전역변수, 블록 변수
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>변수 선언</title></head>
<body>
<h3>변수 선언, 전역/지역/블록 변수</h3>
<hr>
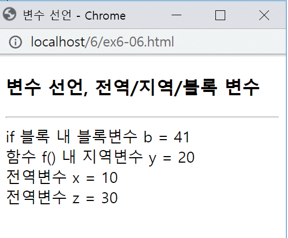
<script>
let x; // 전역 변수 x 선언. var로 선언해도 동일
function f() {
let y; // 함수 f() 내에서만 사용되는 지역 변수 y 선언. var로 선언해도 동일
x = 10; // 전역 변수 x에 10 저장
y = 20; // 지역 변수 y에 20 저장
z = 30; // 새로운 전역 변수 z가 선언되고 30이 저장됨
if(y == 20) {
let b = 40; // if 블록에서만 사용되는 블록 변수 b 선언
b++;
document.write("if 블록 내 블록변수 b = " + b + "<br>");
}
// 이곳에서는 블록 변수 b에 접근할 수 없음
// 이곳에서는 변수 x, y, z에 모두 접근 가능
document.write("함수 f() 내 지역변수 y = " + y + "<br>");
}
f(); // 함수 f() 호출
document.write("전역변수 x = " + x + "<br>");
document.write("전역변수 z = " + z);
// 이곳에서는 변수 x와 z만 접근 가능, 지역 변수 y와 블록 변수 b는 접근 불가
</script>
</body></html>
리터럴 예제
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>리터럴</title></head>
<body>
<h3>리터럴</h3>
<hr>
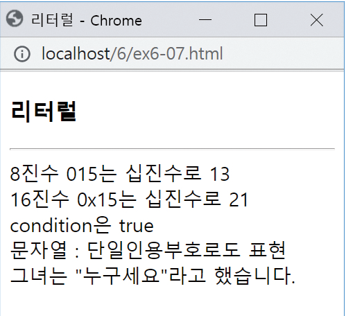
<script>
let oct = 015; // 015는 8진수. 10진수로 13
let hex = 0x15; // 0x14는 16진수. 10진수로 21
let condition = true; // True로 하면 안됨
document.write("8진수 015는 십진수로 " + oct + "<br>");
document.write("16진수 0x15는 십진수로 " + hex + "<br>");
document.write("condition은 " + condition + "<br>");
document.write('문자열 : 단일인용부호로도 표현' + "<br>");
document.write("그녀는 \"누구세요\"라고 했습니다.");
</script>
</body>
</html>
연산자
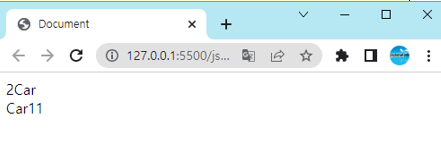
문자열에서의 + 연산자
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body>
<script>
let x, y;
x = 1 + 1 + "Car";
y = "Car" + 1 + 1;
document.write(x + "<br>");
document.write(y + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
산술연산
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>산술연산</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>산술연산</h3>
<hr>
<script>
let x=32;
let total = 100 + x*2/4 - 3; // total은 113
let div = x / 10; // div는 3.2
let mod = x % 2; // x를 2로 나눈 나머지, 0
document.write("x : " + x + "<br><br>");
document.write("100 + x*2/4 - 3 = " + total + "<br>");
document.write("x/10 = " + div + "<br>");
document.write("x%2 = " + mod + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
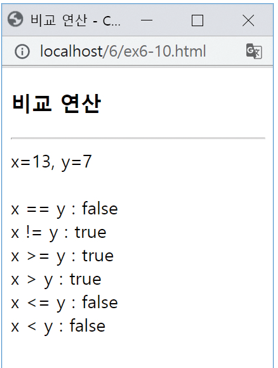
비교연산
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>비교 연산</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>비교 연산</h3>
<hr>
<script>
let x=13, y=7;
document.write("x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "<br><br>");
document.write("x == y : " + (x == y) + "<br>");
document.write("x != y : " + (x != y) + "<br>");
document.write("x >= y : " + (x >= y) + "<br>");
document.write("x > y : " + (x > y) + "<br>");
document.write("x <= y : " + (x <= y) + "<br>");
document.write("x < y : " + (x < y) + "<br>");
</script>
</body>
</html>
논리연산자
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>논리 연산</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>논리 연산</h3>
<hr>
<script>
let x=true, y=false;
document.write("x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "<br><br>");
document.write("x && y : "+ (x&&y) +"<br>");
document.write("x || y : "+ (x||y) +"<br>");
document.write("!x : " + (!x) +"<br>");
document.write("<hr>");
document.write("(3>2) && (3<4) : " + ((3>2)&&(3<4)) + "<br>");
document.write("(3==-2) || (-1<0) : " + ((3==2)||(-1<0)));
</script>
</body>
</html>
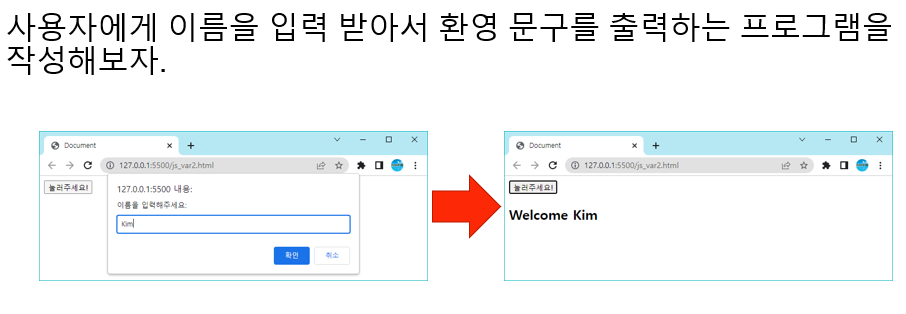
변수에 문자열 저장하기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<script>
function sub() {
const name = prompt('이름을 입력해주세요:');
document.getElementById("test").innerHTML = "Welcome " + name;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="sub()">눌러주세요!</button>
<h2 id=" test"></h2>
</body>
</html>
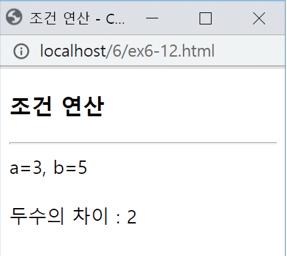
조건연산
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>조건 연산</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>조건 연산</h3>
<hr>
<script>
let a=3, b=5;
document.write("a=" + a + ", b=" + b + "<br><br>");
document.write("두수의 차이 : " + ((a>b)?(a-b):(b-a)));
</script>
</body>
</html>
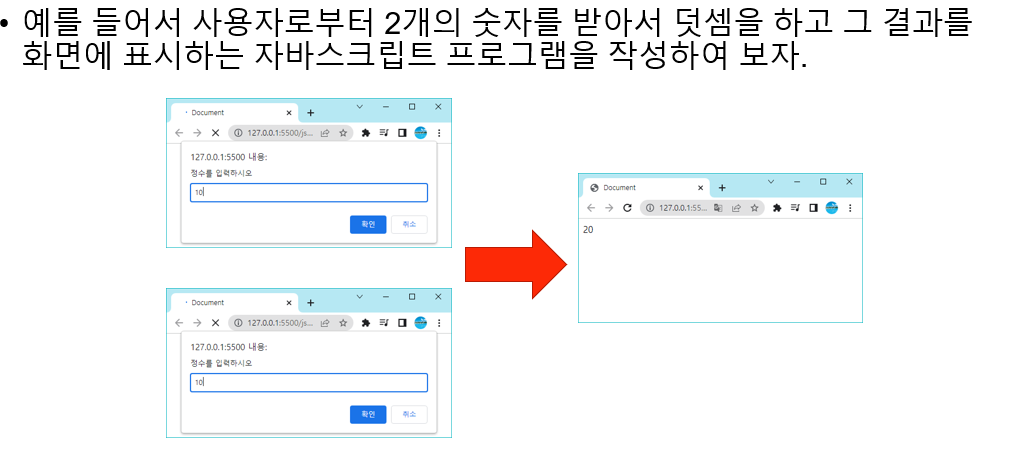
덧셈 프로그램
<script>
let x, y;
let input;
input = prompt("정수를 입력하시오", "정수로");
x = parseInt(input);
input = prompt("정수를 입력하시오", "정수로");
y = parseInt(input);
document.write(x+y + "<br>");
</script>
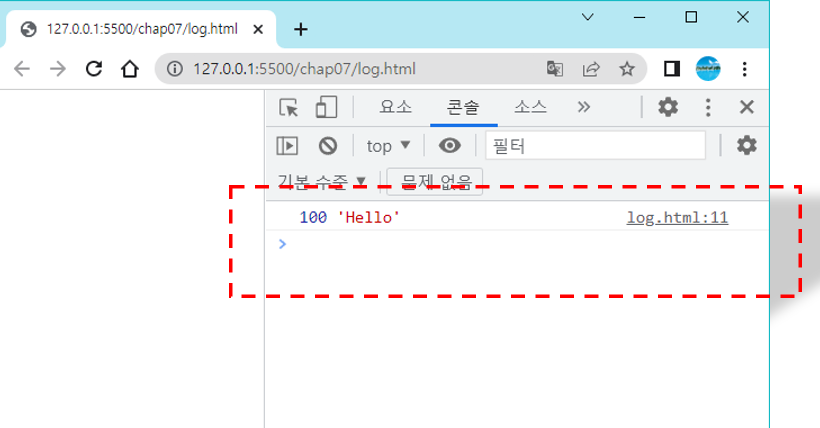
console.log()
자바스크립트 코드를 디버깅할 때 많이 사용하는 함수가 console.log()이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
let x = 100;
let y = 'Hello';
console.log(x, y);
</script>
</body>
</html>
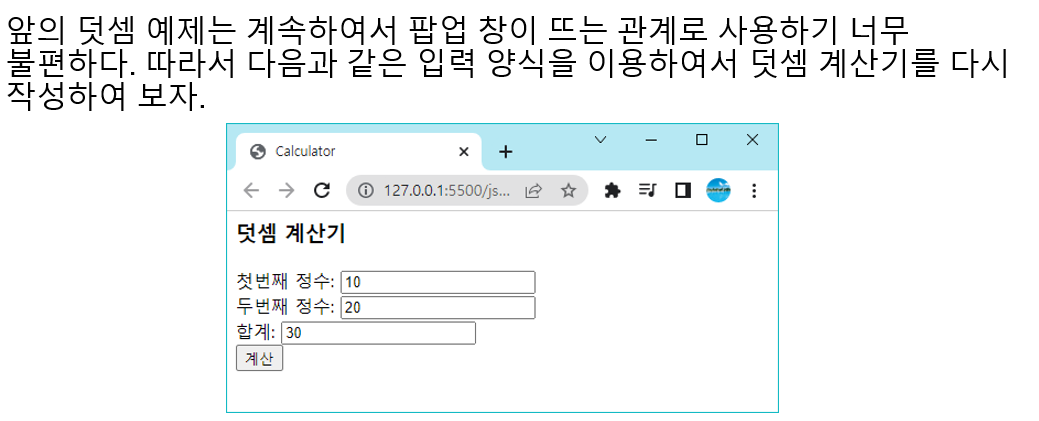
덧셈 프로그램 작성
<html><head>
<title>Calculator</title>
<script>
function calc() {
let x = document.getElementById("x").value;
let y = document.getElementById("y").value;
let sum;
sum = parseInt(x) + parseInt(y);
document.getElementById("sum").value = sum;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>덧셈 계산기</h3>
<form name="myform" action="..." method="POST">
첫번째 정수: <input id="x" /><br />
두번째 정수: <input id="y" /><br />
합계: <input id="sum" /><br />
<input type="button" value="계산" onclick="calc();" />
</form>
</body></html>
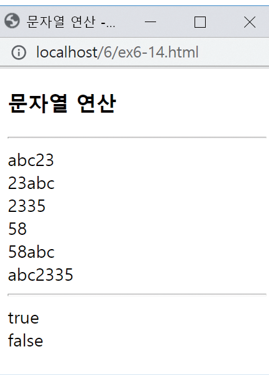
문자열 연산
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>문자열 연산</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>문자열 연산</h3>
<hr>
<script>
document.write("abc" + 23 + "<br>");
document.write(23 + "abc" + "<br>");
document.write(23 + "35" + "<br>");
document.write(23 + 35 + "<br>");
document.write(23 + 35 + "abc" + "<br>");
document.write("abc" + 23 + 35 + "<br><hr>");
let name = "kitae";
document.write(name == "kitae");
document.write("<br>");
document.write(name > "park");
</script>
</body>
</html>


댓글남기기