[자료구조] 큐 - Queues
큐 - Queues
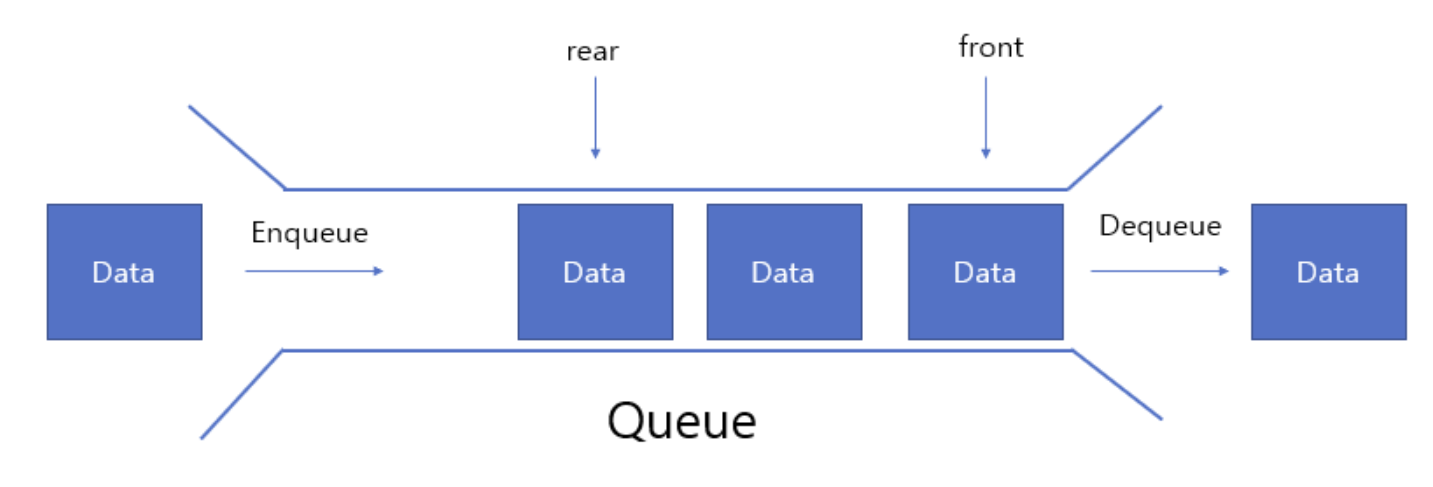
큐는 엔트리가 한쪽 끝(뒤쪽)에 insert되고 다른쪽 끝(앞쪽)에서 제거될 수 있는 순서가 지정된 엔트리의 데이터구조다.
- 특징으로는 선입선출(First-in First-Out)이 있다.
STL Queue Class Template
Queue Class Template는 다음과 같다.
- pop() (dequeue)
- push(const Item& entry) (enqueue)
- empty()
- size()
- front()
- etc.
Queue Errors
Queue overflow
- 꽉찬 천체 대기열에 아이템을 푸시하려고 시도했을때 결과는 큐 오버플로우 에러
Queue underflow
- 빈 대기열에서 아이템을 pop하려고 시도한 결과는 큐 언더플로우 에러
Queue Applications
Recognizing Palindromes(회문 인식하기)
Palindromes(회문) : 앞두로 같은 문자열을 읽는다.
Ex : radar, Able was I ere I saw Elba
스택과 큐를 사용해 문자열이 회문인지 여부를 확인할 수 있다.
// FILE: pal.cpp
// Program to test whether an input line is a palindrome. Spaces,
// punctuation, and the difference between upper- and lowercase are ignored.
#include <cassert> // Provides assert
#include <cctype> // Provides isalpha, toupper
#include <cstdlib> // Provides EXIT_SUCCESS
#include <iostream> // Provides cout, cin, peek
#include <queue> // Provides the queue template class
#include <stack> // Provides the stack template class
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
queue<char> q;
stack<char> s;
char letter;
queue<char>::size_type mismatches = 0; // Mismatches between queue and stack
cout << "Enter a line and I will see if it's a palindrome:" << endl;
while (cin.peek( ) != '\n')
{
cin >> letter;
if (isalpha(letter))
{
q.push(toupper(letter)); //대소문자 무시
s.push(toupper(letter)); //대소문자 무시
}
}
while ((!q.empty( )) && (!s.empty( )))
{
if (q.front( ) != s.top( ))
++mismatches;
q.pop( );
s.pop( );
}
if (mismatches == 0)
cout << "That is a palindrome." << endl;
else
cout << "That is not a palindrome." << endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Queue class의 구현
Array(배열) 구현
배열이 얼마나 많이 사용되었는지 추적하려면 두개의 변수(first, last)가 필요하다.
1. 첫번째 심플한 접근방법
- first - 현재 사용중인 첫 번째 인덱스를 나타낸다.
- last - 현재 사용중인 마지막 인덱스를 나타낸다.
- first와 last는 아이템이 추가되거나 제거될 때 항상 증가한다.
- 문제점 : 배열에 공간이 있어도 마지막 아이템이 끝나면 새 아이템을 추가할 수 없다.
2. 다른 심플한 접근방법
- 맨 앞의 항목이 배열에서 삭제되면 나머지 아이템을 모두 왼쪽으로 한칸 이동해 first는 항상 0이된다.
- 문제점 : 매우 비효율적이다.
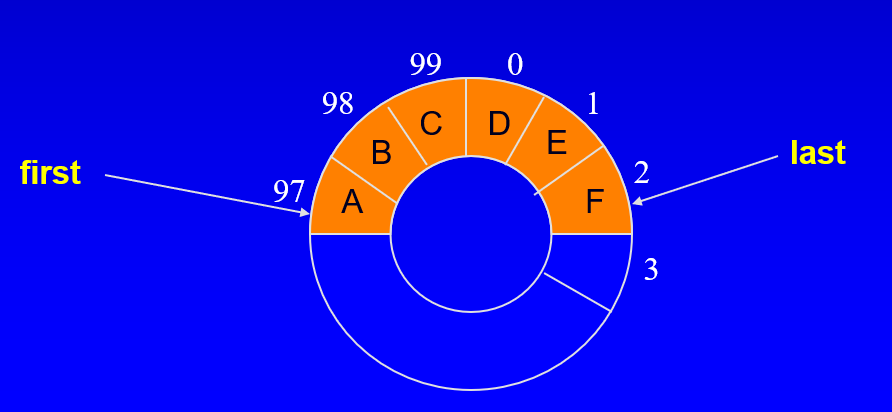
3. 원형 배열 접근방법
- 끝부분 인덱스가 배열의 끝에 도달하면 배열의 전면에서 사용가능한 위치를 재사용할 수 있다.
- 이때 노드를 결정하는 방법은 0~99니까 총 100개 즉 100으로 나눠주고 나머지에 해당한다.
- next_index = (current_index + 1) % CAPACITY
- 이 방법은 first, last, count(꽉찼을때)의 변수를 사용한다.
- 현재 인덱스가 주어진 다음 인덱스를 계산하기 위해 privite 맴버 함수 next_index를 사용한다.
- 빈 큐의 경우 last는 유효한 인덱스고 first는 항상 next_index(last)와 같다.
- 추가설명하자면 1개만 있을때 first와 last가 같은큐고 하나를 pop하면 last는 앞으로 가므로 fisrt는 항상 last다음 인덱스에 있다.
이 방법으로 구현한 코드(헤더와 템플릿파일)는 다음과 같다.
queue_array.h
#ifndef MAIN_SAVITCH_QUEUE1_H
#define MAIN_SAVITCH_QUEUE1_H
#include <cstdlib> // Provides size_t
namespace main_savitch_8B
{
template <class Item>
class queue
{
public:
// TYPEDEFS and MEMBER CONSTANTS -- See Appendix E if this fails to compile.
typedef std::size_t size_type;
typedef Item value_type;
static const size_type CAPACITY = 30;
// CONSTRUCTOR
queue( ); //템플릿 구현
// MODIFICATION MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void pop( ); //템플릿 구현
void push(const Item& entry); //템플릿 구현
// CONSTANT MEMBER FUNCTIONS
bool empty( ) const { return (count == 0); } //바로 구현
Item front( ) const; //템플릿 구현
size_type size( ) const { return count; } //바로구현
private:
Item data[CAPACITY]; // Circular array 초기화
size_type first; // Index of item at front of the queue
size_type last; // Index of item at rear of the queue
size_type count; // Total number of items in the queue
// HELPER MEMBER FUNCTION
size_type next_index(size_type i) const { return (i+1) % CAPACITY; }
};
}
#include "queue_array.template" // Include the implementation.
#endif
queue_array.template
#include <cassert> // Provides assert
namespace main_savitch_8B
{
template <class Item>
const typename queue<Item>::size_type queue<Item>::CAPACITY;
template <class Item>
queue<Item>::queue( )
{
count = 0; //초기상태
first = 0; //처음부분
last = CAPACITY - 1; //last는 마지막을 가르킴
}
template <class Item>
Item queue<Item>::front( ) const
// Library facilities used: cassert
{
assert(!empty( )); //언더플로우 확인
return data[first]; //front는 first에 들어있는 데이터를 리턴
}
template <class Item>
void queue<Item>::pop( )
// Library facilities used: cassert
{
assert(!empty( )); //언더플로우 확인
first = next_index(first); //선입선출으로 first를 다음노드로 이동
// 굳이 데이터 자체를 지우지 않고 first를 이동시켜주는 방식이다
--count; //count 감소
}
template <class Item>
void queue<Item>::push(const Item& entry)
// Library facilities used: cassert
{
assert(size( ) < CAPACITY); //오버플로우 확인
last = next_index(last); //last를 이동시키고
data[last] = entry; //데이터를 집어 넣음
++count; //count 증가
}
}
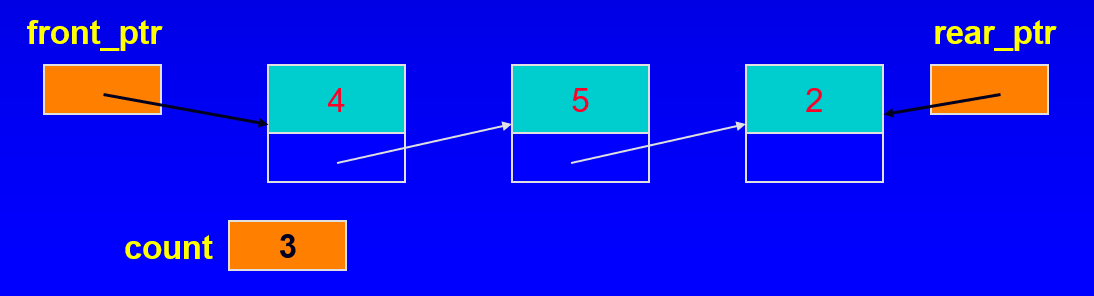
linked list 구현
- 두개의 포인터와 하나의 카운트 변수를 사용한다.
- front_ptr - 첫 번째 노드를 가르킴
- rear_ptr - 마지막 노드를 가르킴
- count - 목록의 아이템 수를 계산함
- 기존에 만든 링크드리스트 헤더파일(node.h)을 include한다. linked list 설명 포스트
queue_linkedList.h
#ifndef MAIN_SAVITCH_QUEUE2_H // Prevent duplicate definition
#define MAIN_SAVITCH_QUEUE2_H
#include <cstdlib> // Provides std::size_t
#include "node.h" // Node template class
namespace main_savitch_8C
{
template <class Item>
class queue
{
public:
// TYPEDEFS
typedef std::size_t size_type;
typedef Item value_type;
// CONSTRUCTORS and DESTRUCTOR
queue( );
queue(const queue<Item>& source);
~queue( );
// MODIFICATION MEMBER FUNCTIONS
void pop( );
void push(const Item& entry);
void operator =(const queue<Item>& source);
// CONSTANT MEMBER FUNCTIONS
bool empty( ) const { return (count == 0); }
Item front( ) const;
size_type size( ) const { return count; }
private:
main_savitch_6B::node<Item> *front_ptr;
main_savitch_6B::node<Item> *rear_ptr;
size_type count; // Total number of items in the queue
};
}
#include "queue_linkedList.template" // Include the implementation
#endif
queue_linkedList.template
#include <cassert> // Provides assert
#include "node.h" // Node template class
namespace main_savitch_8C
{
template <class Item>
queue<Item>::queue( )
{
count = 0;
front_ptr = NULL;
}
template <class Item>
queue<Item>::queue(const queue<Item>& source)
// Library facilities used: node.h
{
count = source.count;
list_copy(source.front_ptr, front_ptr, rear_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
queue<Item>::~queue( )
{
list_clear(front_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
void queue<Item>::operator =(const queue<Item>& source)
// Library facilities used: node.h
{
if (this == &source) // Handle self-assignment
return;
list_clear(front_ptr);
list_copy(source.front_ptr, front_ptr, rear_ptr);
count = source.count;
}
template <class Item>
Item queue<Item>::front( ) const
// Library facilities used: cassert
{
assert(!empty( ));
return front_ptr->data( );
}
template <class Item>
void queue<Item>::pop( )
// Library facilities used: cassert, node.h
{
assert(!empty( ));
list_head_remove(front_ptr);
--count;
}
template <class Item>
void queue<Item>::push(const Item& entry)
// Library facilities used: node.h
{
if (empty( ))
{ // Insert first entry.
list_head_insert(front_ptr, entry);
rear_ptr = front_ptr;
}
else
{ // Insert an entry that is not the first.
list_insert(rear_ptr, entry);
rear_ptr = rear_ptr->link( );
}
++count;
}
}
Priority Queues
Priority 큐는 지정된 우선 순위 수준에 따라 항목을 검색할 수 있는 컨테이너 클래스다.
-“out” 순서는 “in” 순서와 같지 않을 수 있다.
댓글남기기