[자료구조] 트리 - Trees(Part 2)
트리 - Trees(Part 2)
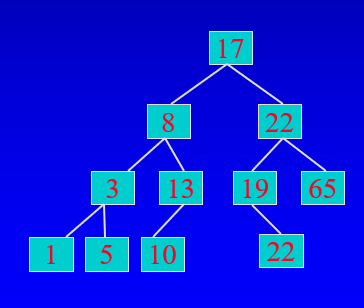
바이너리 서치 트리
바이너리 서치 트리를 BST라고 하자
BST는 다음 속성을 가진다.
- 주어진 노드 N의 왼쪽 서브트리에 있는 모든 데이터 항목은 노드N의 데이터보다 작거나 같다.
- 주어진 노드 N의 오른쪽 서브트리에 있는 모든 데이터 항목은 노드N의 데이터보다 크다.
bag class
BST로 구현된 백 클래스를 알아보자
template<class Item>
class bag
{
public:
…
private:
binary_tree_node<Item>* root_ptr;
}
Member Funtions
BST로 구현된 백클래스의 맴버 함수를 알아보자
| constructor | destructor | insert(entry) |
| erase(target) | erase_one(target) | += , = |
| size( ) | count(target) |
Constructor
- 루트 포인터를 NULL로 설정
Copy Constructor
- 소스 트리의 복사본을 만들고 루트 포인터가 트리를 가리키도록함
Destructor
- 트리의 모든 노드 해제
Size()
- 트리의 노드 수를 계산
- 1 + Size(왼쪽 서브트리) + Size(오른쪽 서브트리)
Assignment Operator
- Self-assignment를 확인하고 그렇다면 리턴
- 현재 트리에서 사용중인 모든 메로리를 헤제
- RHS의 트리를 자신에게 복사
insert(entry)
- 엔트리가 있는 새 노드를 만들고 new_ptr이 가리키도록 함
- 만약 트리가 비어있으면 root_ptr을 new_ptr로 설정
- 그렇지 않으면 적절한 리프노드를 찾을 때까지 바이너리 서치를 수행해 new_ptr을 왼쪽/오른쪽 하위필드의 값으로 만듬
insert(entry) : 바이너리 서치를 하는법
case1 : entry가 node_ptr->data()보다 작거나 같은 경우
-
if node_ptr->left( ) is NULL, node_ptr->set_left(new_ptr) and done
-
else node_ptr = node_ptr->left( ) ;
case2 : entry가 node_ptr->data()보다 큰 경우
-
if node_ptr->right( ) is NULL, node_ptr->set_right(new_ptr) and done
-
else node_ptr = node_ptr->right( ) ;
erase_one(target)
- erase_one을 구현하기 위해 두개의 함수가 필요하다.
- 아래 bst_remove()와 bst_remove_max()를 정의한다.
bst_remove(binary_tree_node
- 트리에서 타겟이 있는 노드를 제거
bst_remove_max(binary_tree_node
- 트리에서 가장 큰 데이터가 있는 노드를 제거
erase_one(target) : 구현
bst_remove(root_ptr, target)
- if / target < root_ptr->data( )인 경우
- bst_remove(root_ptr->left( ),target) 호출
- else / target > root_ptr->data( )인경우
- bst_remove(root_ptr->right( ),target) 호출
- else / target == root_ptr->data( )인 경우에는 2가지 case발생
첫 번째 case : 루트에 왼쪽 자식이 없는경우
- 루트를 삭제하고 올바른 자식을 새 루트로 만듬
- oldroot_ptr = root_ptr ;
- root_ptr = root_ptr->right( ) ;
- delete oldroot_ptr ;
두 번째 case : 루트에 왼쪽 자식이 있는경우
- 왼쪽 서브트리에서 가장 큰 데이터가 있는 노드를 제거하고
- 가장 큰 데이터를 루트에 복사
- bst_remove_max(root_ptr->left( ), root_ptr->data( ));
bst_remove_max(root_ptr, removed_Item)
첫 번째 case : 루트에 오른쪽 자식이 없는경우
- 루트가 가장 큰 데이터를 가지고 있다.
- removed_Item = root_ptr->data( ); // 루트 데이터는 최대임
- oldroot = root_ptr ;
- root_ptr = root_ptr->left( ) ; // 루트의 왼쪽 자식을 새 루트로 생성
- delete oldroot ; //이전루트 삭제
두 번째 case : 루트에 오른쪽 자식이 있는경우
- 가장 큰 데이터는 오른쪽 서브트리에 있음
- bst_remove_max(root_ptr->right( ), removed_Item) ;
+=Operator
- += 연산자를 구현하기 위해 insert_all(tree_ptr)을 정의한다.
- insert_all(tree_ptr) 함수는 소스 트리(tree_ptr가 가리키는)의 각 데이터 항목을 트리에 삽입한다.
insert_all(tree_ptr)
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::insert_all(const binary_tree_node<Item>* tree_ptr)
{
if ( tree_ptr != NULL )
{
insert(tree_ptr->data( )) ;
insert_all (tree_ptr->left( )) ;
insert_all (tree_ptr->right( ) ) ;
}
}
따라서 += Operator는 다음과 같다.
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::operator +=(const bag<Item>& addend) {
if (this == &addend){
binary_tree_node<item>* add_ptr = tree_copy(addend.root_ptr);
insert_all(add_ptr);
tree_clear(add_ptr);
}
else
insert_all(addend.root_ptr);
}
bag class 구현
1.bag.h // FILE: bag.h (part of the namespace main_savitch_10)
#ifndef BAG_H
#define BAG_H
#include <cstdlib> // Provides NULL and size_t
#include "bintree.h" // Provides binary_tree_node and related functions
namespace main_savitch_10
{
template <class Item>
class bag
{
public:
// TYPEDEFS
typedef std::size_t size_type;
typedef Item value_type;
// CONSTRUCTORS and DESTRUCTOR
bag( ) { root_ptr = NULL; }
bag(const bag& source);
~bag( );
// MODIFICATION functions
size_type erase(const Item& target);
bool erase_one(const Item& target);
void insert(const Item& entry);
void operator +=(const bag& addend);
void operator =(const bag& source);
// CONSTANT functions
size_type size( ) const;
size_type count(const Item& target) const;
void debug( ) const { print(root_ptr, 0); }
private:
binary_tree_node<Item> *root_ptr; // Root pointer of binary search tree
void insert_all(binary_tree_node<Item>* addroot_ptr);
};
// NONMEMBER functions for the bag<Item> template class
template <class Item>
bag<Item> operator +(const bag<Item>& b1, const bag<Item>& b2);
}
#include "bag.template" // Include the implementation.
#endif
2.bag.template
// FILE: bag.template
// TEMPLATE CLASS IMPLEMENTED: bag<Item> (see bag.h for documentation)
// INVARIANT of the ADT:
// root_ptr is the root pointer of a binary search tree that contains the
// bag's items.
#include <cassert>
#include <cstdlib>
namespace main_savitch_10
{
template <class Item>
void bst_remove_max(binary_tree_node<Item>*& root_ptr, Item& removed)
// Precondition: root_ptr is a root pointer of a non-empty binary
// search tree.
// Postcondition: The largest item in the binary search tree has been
// removed, and root_ptr now points to the root of the new (smaller)
// binary search tree. The reference parameter, removed, has been set
// to a copy of the removed item.
{
binary_tree_node<Item> *oldroot_ptr;
assert(root_ptr != NULL);
if (root_ptr->right( ) != NULL)
bst_remove_max(root_ptr->right( ), removed);
else
{
removed = root_ptr->data( );
oldroot_ptr = root_ptr;
root_ptr = root_ptr->left( );
delete oldroot_ptr;
}
}
template <class Item>
bool bst_remove(binary_tree_node<Item>*& root_ptr, const Item& target)
// Precondition: root_ptr is a root pointer of a binary search tree
// or may be NULL for an empty tree).
// Postcondition: If target was in the tree, then one copy of target
// has been removed, and root_ptr now points to the root of the new
// (smaller) binary search tree. In this case the function returns true.
// If target was not in the tree, then the tree is unchanged (and the
// function returns false).
{
binary_tree_node<Item> *oldroot_ptr;
if (root_ptr == NULL)
{ // Empty tree
return false;
}
if (target < root_ptr->data( ))
{ // Continue looking in the left subtree
return bst_remove(root_ptr->left( ), target);
}
if (target > root_ptr->data( ))
{ // Continue looking in the right subtree
return bst_remove(root_ptr->right( ), target);
}
if (root_ptr->left( ) == NULL)
{ // Target was found and there is no left subtree, so we can
// remove this node, making the right child be the new root.
oldroot_ptr = root_ptr;
root_ptr = root_ptr->right( );
delete oldroot_ptr;
return true;
}
// If code reaches this point, then we must remove the target from
// the current node. We'll actually replace this target with the
// maximum item in our left subtree.
bst_remove_max(root_ptr->left( ), root_ptr->data( ));
return true;
}
template <class Item>
typename bag<Item>::size_type bst_remove_all
(binary_tree_node<Item>*& root_ptr, const Item& target)
// Precondition: root_ptr is a root pointer of a binary search tree
// or may be NULL for an empty tree).
// Postcondition: All copies of target have been removed from the tree
// has been removed, and root_ptr now points to the root of the new
// (smaller) binary search tree. The return value tells how many copies
// of the target were removed.
{
binary_tree_node<Item> *oldroot_ptr;
if (root_ptr == NULL)
{ // Empty tree
return 0;
}
if (target < root_ptr->data( ))
{ // Continue looking in the left subtree
return bst_remove_all(root_ptr->left( ), target);
}
if (target > root_ptr->data( ))
{ // Continue looking in the right subtree
return bst_remove_all(root_ptr->right( ), target);
}
if (root_ptr->left( ) == NULL)
{ // Target was found and there is no left subtree, so we can
// remove this node, making the right child be the new root.
oldroot_ptr = root_ptr;
root_ptr = root_ptr->right( );
delete oldroot_ptr;
return 1;
}
// If code reaches this point, then we must remove the target from
// the current node. We'll actually replace this target with the
// maximum item in our left subtree. We then continue
// searching for more copies of the target to remove.
// This continued search must start at the current root (since
// the maximum element that we moved up from our left subtree
// might also be a copy of the target).
bst_remove_max(root_ptr->left( ), root_ptr->data( ));
return 1 + bst_remove_all(root_ptr, target);
}
template <class Item>
bag<Item>::bag(const bag<Item>& source)
// Library facilities used: bintree.h
{
root_ptr = tree_copy(source.root_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
bag<Item>::~bag( )
// Header file used: bintree.h
{
tree_clear(root_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
typename bag<Item>::size_type bag<Item>::size( ) const
// Header file used: bintree.h
{
return tree_size(root_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::insert(const Item& entry)
// Header file used: bintree.h
{
binary_tree_node<Item> *cursor = root_ptr;
bool done = false;
if (root_ptr == NULL)
{
root_ptr = new binary_tree_node<Item>(entry);
return;
}
do
{
if (cursor->data( ) >= entry)
{ // Go left
if (cursor->left( ) == NULL)
{
cursor->set_left( new binary_tree_node<Item>(entry) );
done = true;
}
else
cursor = cursor->left( );
}
else
{ // Go right
if (cursor->right( ) == NULL)
{
cursor->set_right( new binary_tree_node<Item>(entry) );
done = true;
}
else
cursor = cursor->right( );
}
} while (!done);
}
template <class Item>
typename bag<Item>::size_type bag<Item>::count(const Item& target) const
{
size_type answer = 0;
binary_tree_node<Item> *cursor = root_ptr;
while (cursor != NULL)
{
if (cursor->data( ) < target)
cursor = cursor->right( );
else
{
if (cursor->data( ) == target) answer++;
cursor = cursor->left( );
}
}
return answer;
}
template <class Item>
typename bag<Item>::size_type bag<Item>::erase(const Item& target)
{
return bst_remove_all(root_ptr, target);
}
template <class Item>
bool bag<Item>::erase_one(const Item& target)
{
return bst_remove(root_ptr, target);
}
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::operator =(const bag<Item>& source)
// Header file used: bintree.h
{
if (root_ptr == source.root_ptr)
return;
tree_clear(root_ptr);
root_ptr = tree_copy(source.root_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::operator +=(const bag<Item>& addend)
{
if (root_ptr == addend.root_ptr)
{
bag<Item> copy = addend;
insert_all(copy.root_ptr);
}
else
insert_all(addend.root_ptr);
}
template <class Item>
bag<Item> operator +(const bag<Item>& b1, const bag<Item>& b2)
{
bag<Item> answer = b1;
answer += b2;
return answer;
}
template <class Item>
void bag<Item>::insert_all(binary_tree_node<Item>* addroot_ptr)
// Precondition: addroot_ptr is the root pointer of a binary search tree that
// is separate for the binary search tree of the bag that activated this
// method.
// Postcondition: All the items from the addroot_ptr's binary search tree
// have been added to the binary search tree of the bag that activated this
// method.
{
if (addroot_ptr != NULL)
{
insert(addroot_ptr->data( ));
insert_all(addroot_ptr->left( ));
insert_all(addroot_ptr->right( ));
}
}
}
3.bintree.h
#ifndef BINTREE_H
#define BINTREE_H
#include <cstdlib> // Provides NULL and size_t
namespace main_savitch_10
{
template <class Item>
class binary_tree_node
{
public:
// TYPEDEF
typedef Item value_type;
// CONSTRUCTOR
binary_tree_node(
const Item& init_data = Item( ),
binary_tree_node* init_left = NULL,
binary_tree_node* init_right = NULL
)
{
data_field = init_data;
left_field = init_left;
right_field = init_right;
}
// MODIFICATION MEMBER FUNCTIONS
Item& data( ) { return data_field; }
binary_tree_node*& left( ) { return left_field; }
binary_tree_node*& right( ) { return right_field; }
void set_data(const Item& new_data) { data_field = new_data; }
void set_left(binary_tree_node* new_left) { left_field = new_left; }
void set_right(binary_tree_node* new_right) { right_field = new_right; }
// CONST MEMBER FUNCTIONS
const Item& data( ) const { return data_field; }
const binary_tree_node* left( ) const { return left_field; }
const binary_tree_node* right( ) const { return right_field; }
bool is_leaf( ) const
{ return (left_field == NULL) && (right_field == NULL); }
private:
Item data_field;
binary_tree_node *left_field;
binary_tree_node *right_field;
};
// NON-MEMBER FUNCTIONS for the binary_tree_node<Item>:
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void inorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr);
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void preorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr);
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void postorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr);
template <class Item, class SizeType>
void print(binary_tree_node<Item>* node_ptr, SizeType depth);
template <class Item>
void tree_clear(binary_tree_node<Item>*& root_ptr);
template <class Item>
binary_tree_node<Item>* tree_copy(const binary_tree_node<Item>* root_ptr);
template <class Item>
std::size_t tree_size(const binary_tree_node<Item>* node_ptr);
}
#include "bintree.template"
#endif
4.bintree.template
// FILE: bintree.template
// IMPLEMENTS: The binary_tree node class (see bintree.h for documentation).
#include <cassert> // Provides assert
#include <cstdlib> // Provides NULL, std::size_t
#include <iomanip> // Provides std::setw
#include <iostream> // Provides std::cout
namespace main_savitch_10
{
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void inorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
if (node_ptr != NULL)
{
inorder(f, node_ptr->left( ));
f( node_ptr->data( ) );
inorder(f, node_ptr->right( ));
}
}
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void postorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
if (node_ptr != NULL)
{
postorder(f, node_ptr->left( ));
postorder(f, node_ptr->right( ));
f(node_ptr->data( ));
}
}
template <class Process, class BTNode>
void preorder(Process f, BTNode* node_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
if (node_ptr != NULL)
{
f( node_ptr->data( ) );
preorder(f, node_ptr->left( ));
preorder(f, node_ptr->right( ));
}
}
template <class Item, class SizeType>
void print(binary_tree_node<Item>* node_ptr, SizeType depth)
// Library facilities used: iomanip, iostream, stdlib
{
if (node_ptr != NULL)
{
print(node_ptr->right( ), depth+1);
std::cout << std::setw(4*depth) << ""; // Indent 4*depth spaces.
std::cout << node_ptr->data( ) << std::endl;
print(node_ptr->left( ), depth+1);
}
}
template <class Item>
void tree_clear(binary_tree_node<Item>*& root_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
binary_tree_node<Item>* child;
if (root_ptr != NULL)
{
child = root_ptr->left( );
tree_clear( child );
child = root_ptr->right( );
tree_clear( child );
delete root_ptr;
root_ptr = NULL;
}
}
template <class Item>
binary_tree_node<Item>* tree_copy(const binary_tree_node<Item>* root_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
binary_tree_node<Item> *l_ptr;
binary_tree_node<Item> *r_ptr;
if (root_ptr == NULL)
return NULL;
else
{
l_ptr = tree_copy( root_ptr->left( ) );
r_ptr = tree_copy( root_ptr->right( ) );
return
new binary_tree_node<Item>( root_ptr->data( ), l_ptr, r_ptr);
}
}
template <class Item>
size_t tree_size(const binary_tree_node<Item>* node_ptr)
// Library facilities used: cstdlib
{
if (node_ptr == NULL)
return 0;
else
return
1 + tree_size(node_ptr->left( )) + tree_size(node_ptr->right( ));
}
}
5.bagtest.cpp
// FILE: bagtest.cxx
// Written by Michael Main (main@colorado.edu) - Nov 8, 2000
// An interactive test program for the new Bag class, implemented with
// a binary search tree.
#include <cctype> // Provides toupper
#include <iostream> // Provides cout, cin
#include <cstdlib> // Provides EXIT_SUCCESS, size_t
#include "bag.h" // Provides the bag<double> class (with Item as a double)
using namespace std;
using namespace main_savitch_10;
// PROTOTYPES for the functions used in this test program.
void print_menu( );
// Postcondition: A menu of choices for this program has been written to cout.
char get_user_command( );
// Postcondition: The user has been prompted to enter a one character command.
// A line of input (with at least one character) has been read, and the first
// character of the input line is returned.
void display_bags(const bag<double>& b1, const bag<double>& b2);
// Postcondition: The function has tested whether the numbers 0..9 are in
// the two bags, and printed the results to standard output.
bag<double> copybag(bag<double> b);
// Postcondition: The return value is a copy of b.
double get_number( );
// Postcondition: The user has been prompted to enter a double number. The
// number has been read, echoed to the screen, and returned by the function.
int main( )
{
bag<double> b1, b2; // Bags that we'll perform tests on
char choice; // A command character entered by the user
cout << "I have initialized two empty bags of doubles." << endl;
do
{
print_menu( );
choice = get_user_command( );
switch (choice)
{
case 'A': b1 = b2;
break;
case 'a': b2 = b1;
break;
case 'C': b1 = copybag(b2);
break;
case 'c': b2 = copybag(b1);
break;
case 'S':
case 's': cout << "The bags' sizes are " << b1.size( );
cout << " and " << b2.size( ) << endl;
break;
case 'I': b1.insert(get_number( ));
break;
case 'i': b2.insert(get_number( ));
break;
case 'O': b1.erase_one(get_number( ));
break;
case 'o': b2.erase_one(get_number( ));
break;
case 'E': b1.erase(get_number( ));
break;
case 'e': b2.erase(get_number( ));
break;
case 'D':
case 'd': display_bags(b1, b2);
break;
case 'q':
case 'Q': cout << "Ridicule is the best test of truth." << endl;
break;
default: cout << choice << " is invalid. Sorry." << endl;
}
}
while ((toupper(choice) != 'Q'));
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
void print_menu( )
// Library facilties used: iostream.h
{
cout << "The following choices are available with 2 bags: " << endl;
cout << " A Use the assignment operator to make b1 equal to b2" << endl;
cout << " a Use the assignment operator to make b2 equal to b1" << endl;
cout << " C Use the copy constructor to make b1 equal to b2" << endl;
cout << " c Use the copy constructor to make b2 equal to b1" << endl;
cout << " I Insert an item into b1" << endl;
cout << " i Insert an item into b2" << endl;
cout << " E Erase item from b1" << endl;
cout << " e Erase item from b2" << endl;
cout << " O Erase one item from b1" << endl;
cout << " o Erase one item from b2" << endl;
cout << " D Display a count of items 0-9 in b1 and b2" << endl;
cout << " S Print the result from the size( ) functions" << endl;
cout << " Q Quit this test program" << endl;
}
char get_user_command( )
// Library facilties used: iostream.h
{
char command;
cout << "Enter choice: ";
cin >> command;
return command;
}
void display_bags(const bag<double>& b1, const bag<double>& b2)
// Library facilties used: iostream.h
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << i << " in b1? " << b1.count(i);
cout << " " << i << " in b2? " << b2.count(i) << endl;
}
}
bag<double> copybag(bag<double> b)
{
return b;
}
double get_number( )
// Library facilties used: iostream.h
{
int result;
cout << "Please enter a double number for the bag: ";
cin >> result;
cout << result << " has been read." << endl;
return result;
}
댓글남기기